The DMAIC methodology, a structured approach to problem-solving and process improvement, has become a cornerstone of Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing. For Supplier Quality Engineers (SQEs), DMAIC offers a powerful framework to identify, analyze, and eliminate defects in supplier processes, ultimately enhancing product quality and reducing costs.
Understanding DMAIC
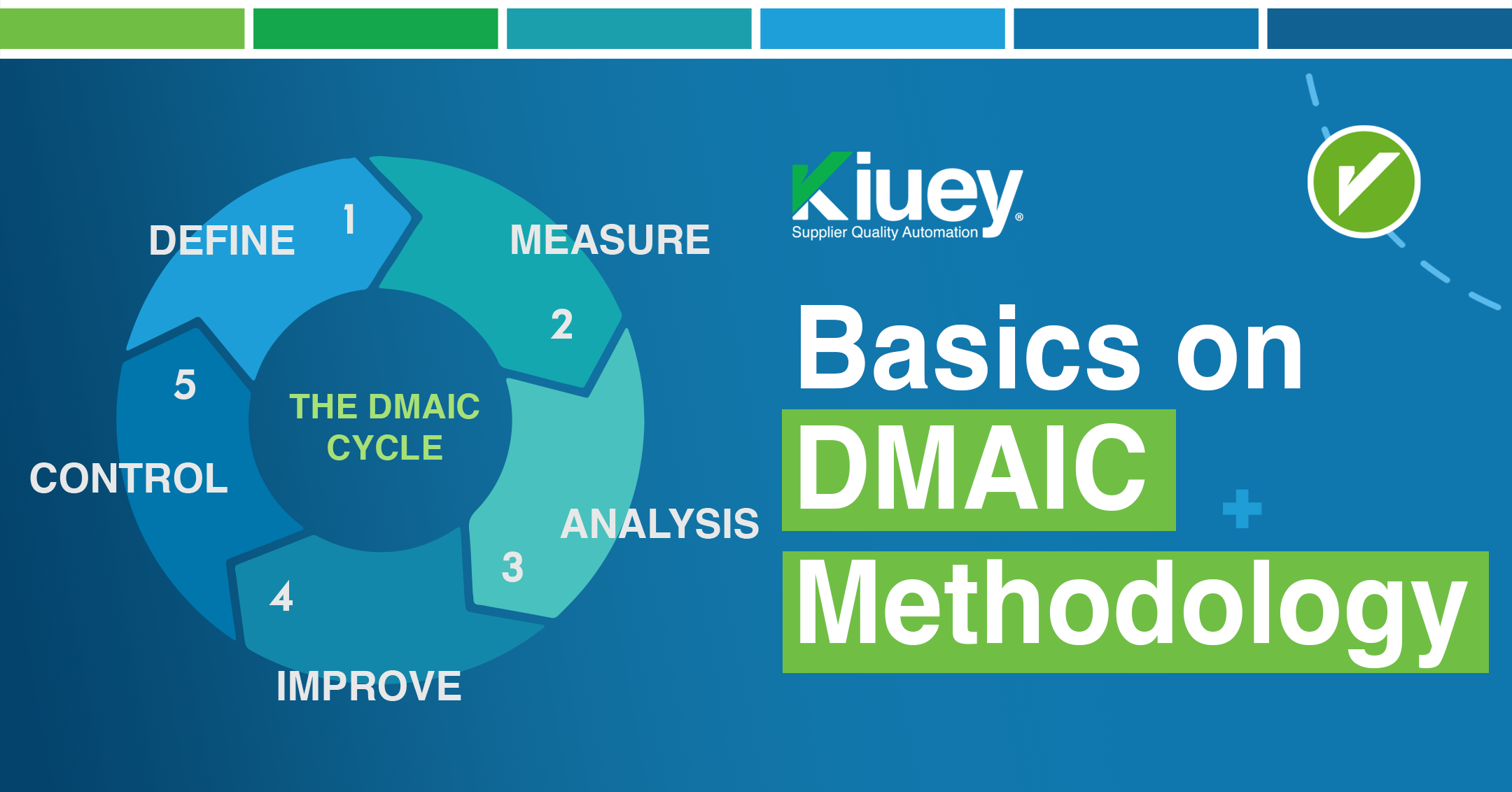
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Each phase of this methodology serves a distinct purpose:
- Define: This initial phase involves clearly identifying the problem or opportunity for improvement. SQEs must define the scope of the project, set goals, and create a project charter.
- Measure: Once the problem is defined, the next step is to collect data to understand the current state of the process. SQEs use various tools, such as control charts, histograms, and Pareto diagrams, to gather and analyze quantitative and qualitative data.
- Analyze: In this phase, SQEs delve deeper into the data to identify the root causes of the problem. Tools like fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys analysis, and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) are employed to uncover the underlying issues.
- Improve: With a clear understanding of the root causes, SQEs can develop and implement solutions to address the problem. This may involve process modifications, changes in materials, or improvements in supplier capabilities.
- Control: The final phase focuses on sustaining the improvements achieved. SQEs establish control plans to monitor the process and prevent regression. This may include implementing new procedures, training employees, or using statistical process control (SPC) techniques.
DMAIC in Action for SQEs
SQEs can apply the DMAIC methodology to a wide range of supplier quality issues, such as:
- Reducing defects: By identifying and eliminating the root causes of defects, SQEs can significantly improve product quality and reduce rework costs.
- Improving process efficiency: DMAIC helps SQEs streamline supplier processes, reducing cycle times and improving overall productivity.
- Strengthening supplier relationships: By demonstrating a commitment to continuous improvement, SQEs can build stronger relationships with suppliers and foster a culture of collaboration.
- Cost reduction: By identifying and eliminating waste in the supply chain, SQEs can help reduce costs and improve profitability.
Key Tools and Techniques
SQEs can leverage various tools and techniques within the DMAIC framework, including:
- Statistical process control (SPC): SPC helps monitor process variation and identify when a process is out of control.
- Root cause analysis: Techniques like the 5 Whys and fishbone diagrams help SQEs uncover the underlying causes of problems.
- Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA): FMEA is used to identify potential failures in a process and assess their risk.
- Design of experiments (DOE): DOE can be used to optimize processes by testing different variables and identifying their impact on the outcome.
Benefits of DMAIC for SQEs
By effectively applying the DMAIC methodology, SQEs can achieve several benefits, including:
- Improved product quality: Reduced defects and higher customer satisfaction.
- Increased efficiency: Streamlined processes and reduced cycle times.
- Cost savings: Lower costs associated with rework, scrap, and waste.
- Enhanced supplier relationships: Stronger collaboration and trust.
- Career advancement: Demonstrated problem-solving and process improvement skills.
In conclusion, the DMAIC methodology offers a powerful framework for SQEs to address supplier quality issues and drive continuous improvement. By systematically defining problems, collecting data, analyzing root causes, implementing solutions, and controlling the process, SQEs can enhance product quality, reduce costs, and strengthen supplier relationships.
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Your go-to destination for insights, best practices, and innovative solutions in supplier quality assurance.
Categories
Let's talk to see how PPAP Manager can help your company to save time and money.




